The country & thematic pages produced by the European Commission's Civil Protection and Humanitarian Aid Operations department provide overviews on specific themes or geographical areas.
All pages listed below are updated regularly, with their latest revision date indicated on each page.
Filter by
Country & thematic pages (94)
RSS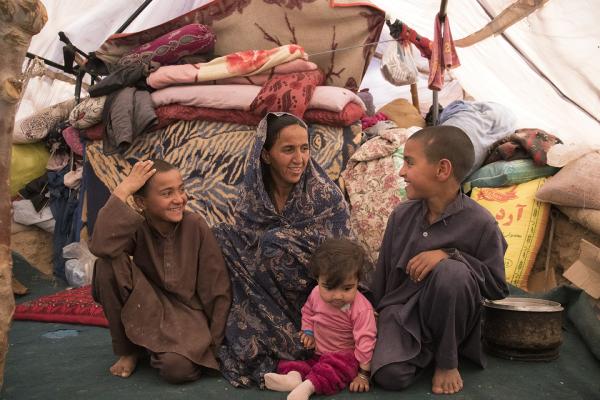
After decades of conflict, natural hazards and chronic poverty, Afghanistan is facing one of the world’s largest and most complex humanitarian crises, which has also far-reaching impacts on neighbouring Iran and Pakistan.
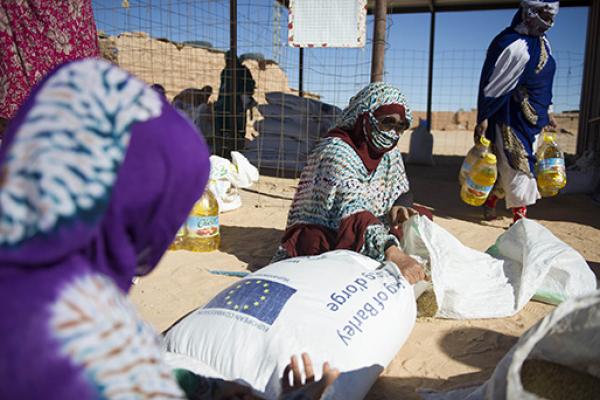

The political conflict in Western Sahara, unresolved for over 4 decades, has left thousands of Sahrawi refugees stranded. They live in 5 isolated camps near Tindouf in south-west Algeria with difficult access to resources, which makes humanitarian aid essential to their survival.

The 6-week-long 2020 war in and around Nagorno-Karabakh resulted in severe consequences for the inhabitants of the region. Last year, the escalation and subsequent ceasefire led to mass exodus of people from Nagorno-Karabakh.
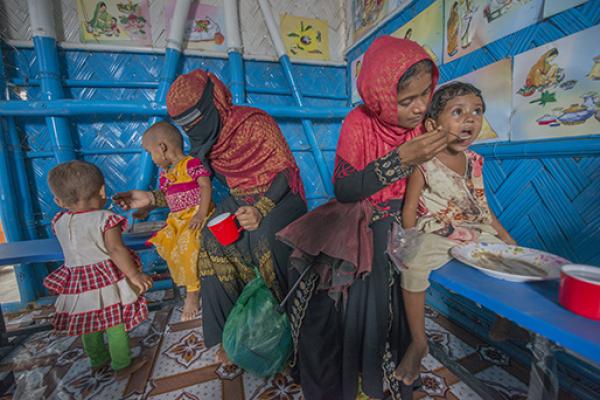

Bangladesh is currently home to over 1 million Rohingya refugees who have fled targeted violence, large-scale armed attacks, and human rights violations in neighbouring Myanmar.
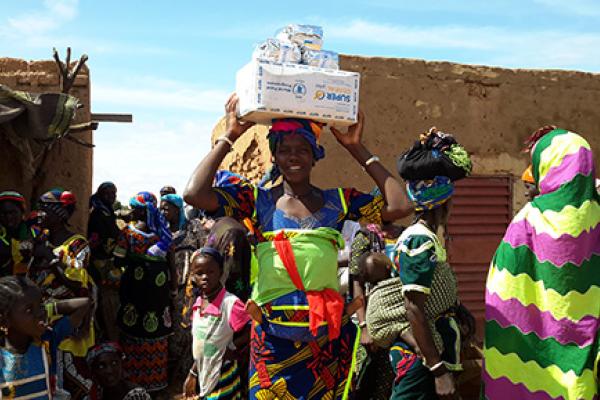

Burkina Faso's complex and volatile crisis continues to deteriorate quickly and severely. The internal conflict has intensified, spreading across all regions of the country. Armed violence is increasingly targeting civilians and has caused massive population displacements.
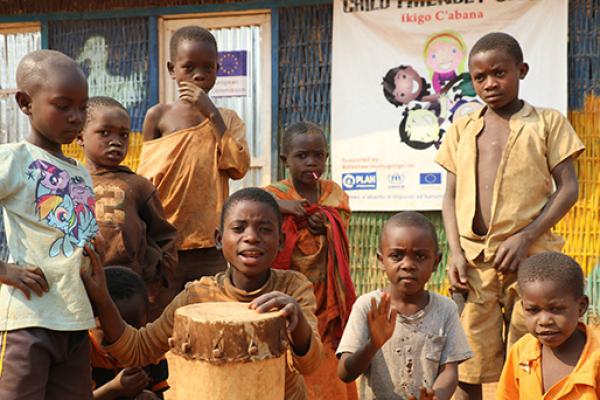

Over 260,000 Burundian refugees remain displaced in neighbouring countries, with most of them having fled Burundi after contested elections and violence in 2015.
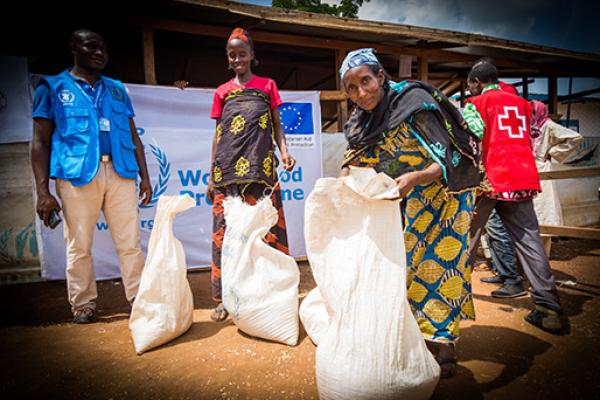

9 out of 10 regions in Cameroon are in the grip of 3 complex and separate humanitarian crises: (i) Lake Chad crisis in the country’s Far North, (ii) the Anglophone crisis in the North-West and South-West regions, and a refugee crisis (iii) from the neighbouring Central African Republic.
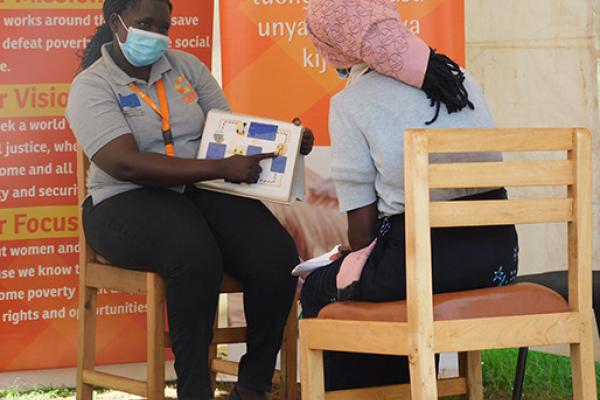

Through capacity building, humanitarian organisations share knowledge, expertise and good practices to react better and faster to emergencies. In turn, working in a coordinated and complementary way will help them respond to humanitarian needs effectively and efficiently.
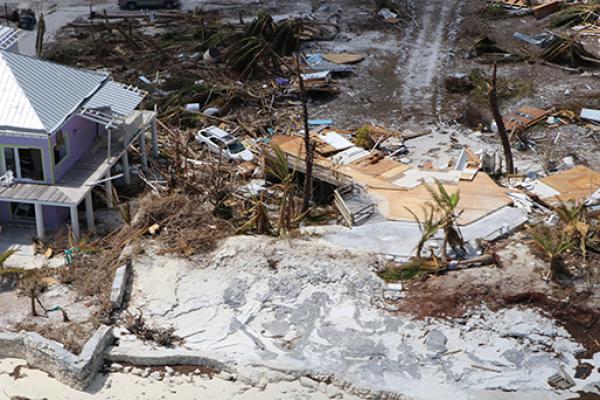

The Caribbean is the second most disaster-prone region in the world, regularly hit by disasters. Its Small Islands Developing States are increasingly vulnerable to climatic events, which are becoming more intense, unpredictable, and frequent, resulting largely from the impacts of climate change.
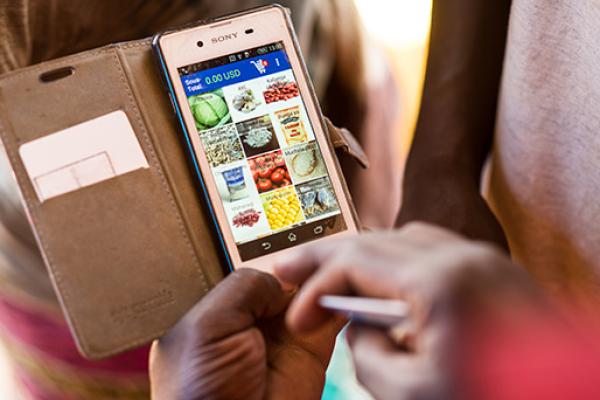

The cash transfers are assistance in the form of money - either physical currency or e-cash.
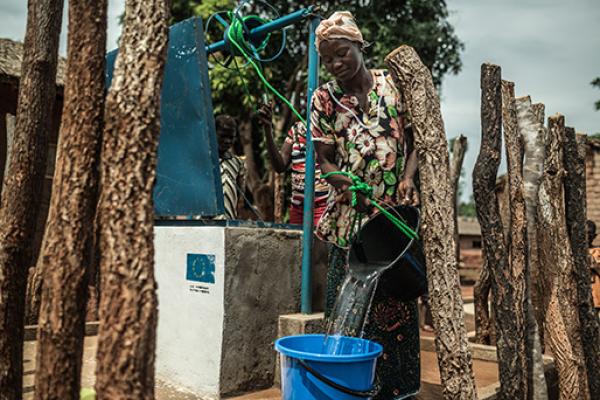

Since the December 2020 presidential elections, the Central African Republic (CAR) is torn by violence opposing armed groups against government forces.
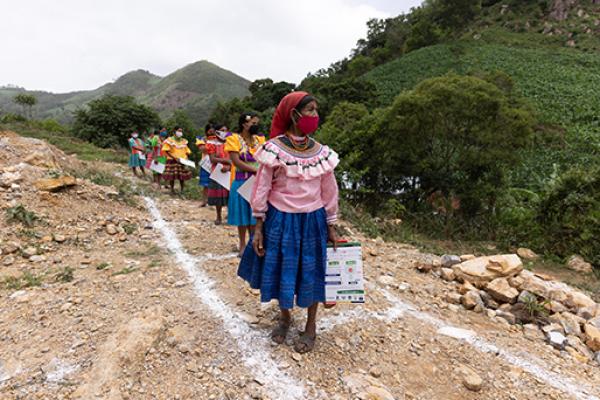

In Central America and Mexico, natural hazards, violence, and displacement have all exacerbated the ongoing humanitarian crisis. The United Nations estimates that about a quarter of the region’s population requires humanitarian aid – an 80% rise from 2020.
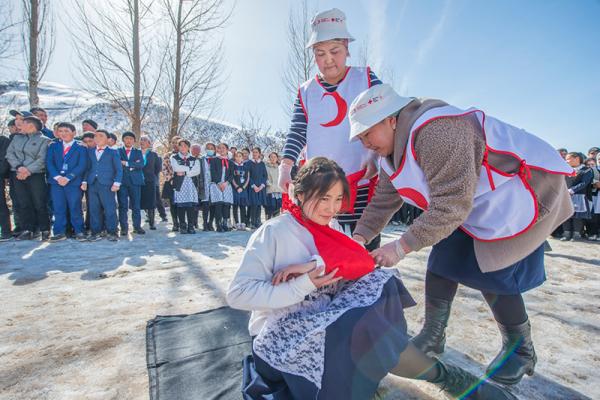

The Central Asia region comprises the countries of Kazakhstan, the Kyrgyz Republic, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. It is prone to natural hazards and particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change.
Chad is one of the poorest countries in the world, marked by low development, very limited availability of basic social services, and exposure to climate and environmental hazards.
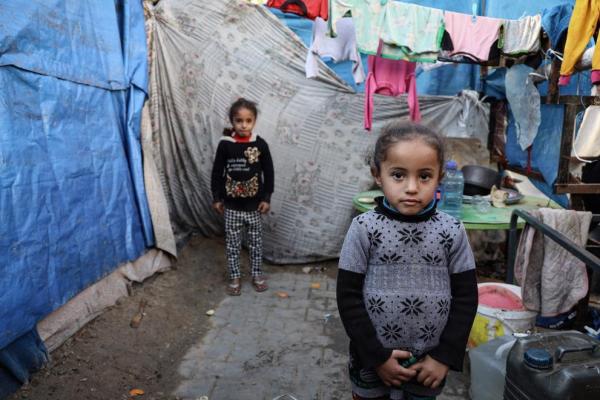

The EU is committed to protect children caught in armed conflicts and to ensure that their needs and rights are respected and fulfilled.
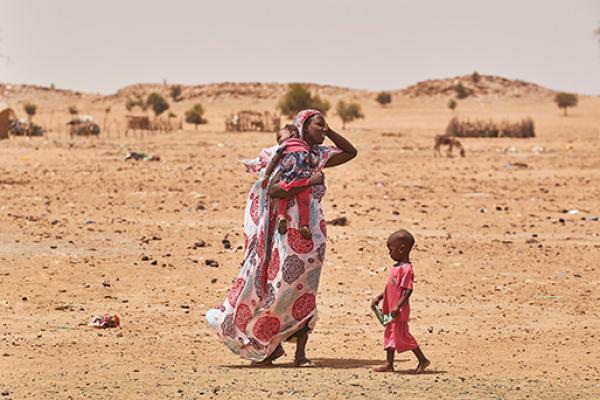

Climate change affects millions of people worldwide, deteriorates the humanitarian situation, and multiplies the needs of vulnerable communities. It alters the earth's temperatures and weather patterns, leading to global warming and increased frequency, scale and duration of extreme weather events.
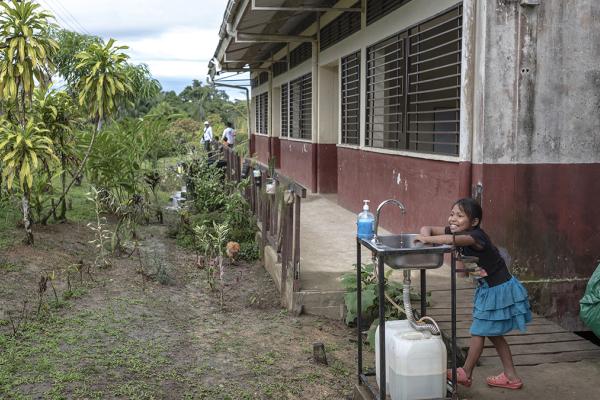

Despite significant development gains in Colombia over the past decade, including the 2016 Peace Agreement with the country’s largest guerrilla group (the FARC), humanitarian needs are still rising.
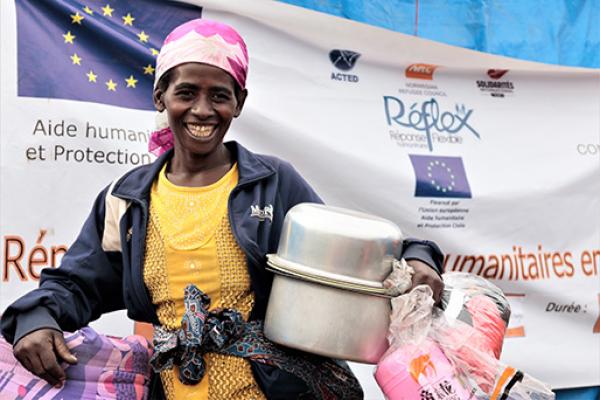

Between conflict, poverty, malnutrition and frequent disease outbreaks, humanitarian needs in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) are among the highest in the world.
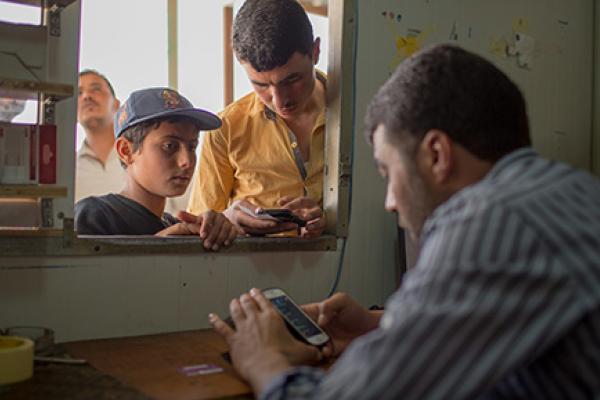

Digital technologies are a key enabler in delivering effective and timely humanitarian aid. They allow humanitarian organisations to improve collaboration and communication, deliver aid more efficiently and make the emergency response targeted to the needs of the beneficiaries.
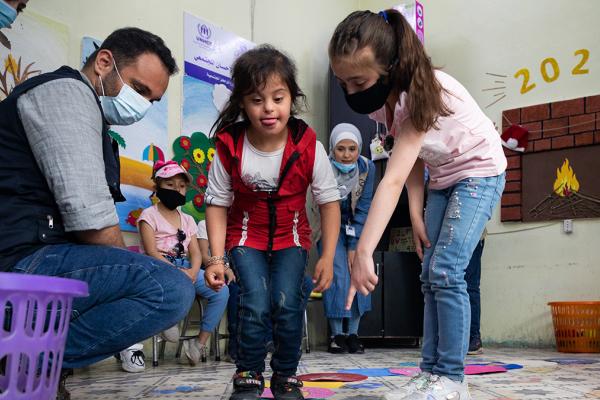

People with disabilities include those who have long-term physical, mental, intellectual or sensory impairments which may hinder their full and effective participation in society.
